Scientists say they have witnessed a type of replication not previously seen in organic robots created in a laboratory using frog cells. Researchers hope that someday these xenobots, described by the same team in an article published nearly two years ago, could be programmed to perform useful functions, such as detecting cancer cells in humans or trapping harmful microplastics in the ocean. Researchers hope that these xenobots and their self-replicating ability will one day be used for the benefit of humanity. And then these new xenobots can search for cells and create copies of themselves.
The same team that built the first living robots (“Xenobots” harvested from frog cells – reported in 2020) found that these computer-designed, hand-picked organisms could swim in their tiny plate, find individual cells, and collect hundreds of of them. together and gather the Xenobots ‘babies’ in their Pacman ‘mouth’, who in a few days will become the new Xenobots that look and move just like them. Xenobots move using tiny hair-like structures known as cilia. Xenobots are a collection of living cells that do not have a brain or digestive system. But in a sense, they can be programmed to block other cells, as in this study, or perhaps do other things.
In essence, robots are man-made versions of animal life: they are machines that replicate the behavior of humans and animals. More broadly, robotics is a technical discipline related to the design, construction, and operation of robots. A robot is an automated machine that can perform specific tasks with speed and accuracy with little or no human intervention. A robot is a computer programmed to automatically perform one or more tasks with power and agility.
Types of robots? There are as many different types of robots as there are activities. And, there are as many types of robots as the tasks they must perform. Pre-programmed robots operate in a controlled environment, where they perform simple and repetitive tasks.
These robots usually perform human-like actions (such as running, jumping, and carrying objects), and are sometimes even designed to look like us, even with human faces and expressions. Humanoid robots are robots that resemble and/or imitate human behavior. A robot, any mechanically powerful computer, can replace human activities, although it may not look like a human or perform human functions in behavior. According to this definition, what distinguishes robots from other mobile machines (such as cars) lies in their computer elements.
It sounds very simple, but a human engineer cannot come up with such a thing. In 1961, Condec Corp. (after purchasing Unimation last year) delivered the world’s first robot for a production line to the GM plant; it had the unpleasant (for humans) task of removing and stacking hot metal parts from an injection molding machine. Stanford’s Victor Sheinman partnered with Unimation for GM to develop the first arm of this type used in industry. More advanced computer-controlled, touch-driven electric hands were developed in the late 1960s and 1970s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Stanford University, where they were used with cameras to research hand-eye robotic devices.
He envisioned machines that could make copies of the basic parts of robots, explains Sam Krigman, a researcher at the Wyss Institute and lead author of the article.
Using a robotic conveyor belt for bacterial genetics makes the job of scientists less complicated and time-consuming at University College Cork “Robotic conveyor belt” used in bacterial genetics at University College Cork, Cork, Ireland.
Robots can be modern intelligent devices that are used with direct human intervention to aid pilots or control spacecraft.
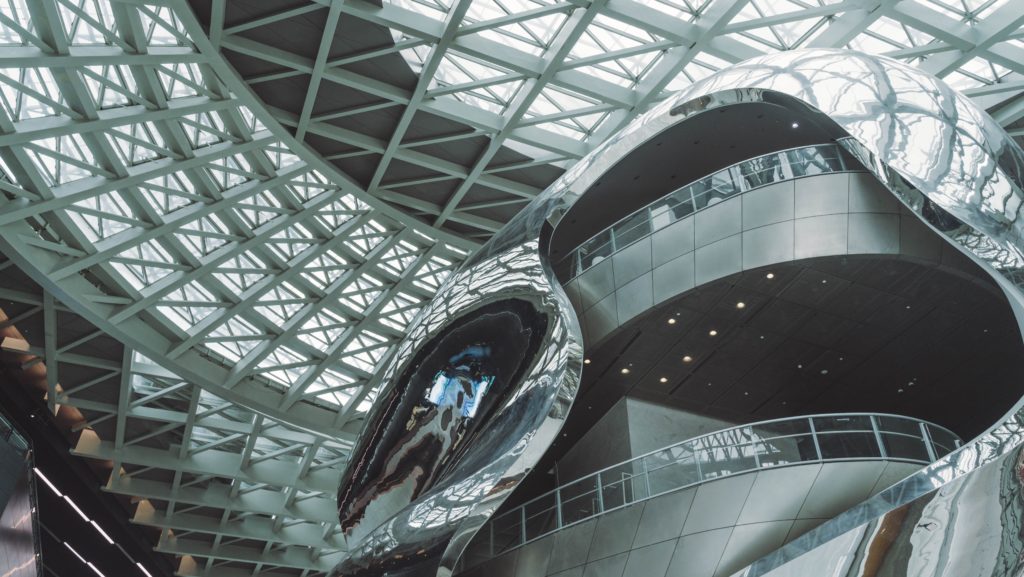

But robots depend on human programming and (probably) always will. The combination of these robots with artificial intelligence has helped companies move from simple automation to higher-level and more complex tasks.
By using robots on aircraft production lines, Airbus aims to alleviate some of the most time-consuming and risky tasks that operators face. Modern robotic technology can only automate 25% of tasks in unpredictable and human-dependent areas such as construction and maintenance.
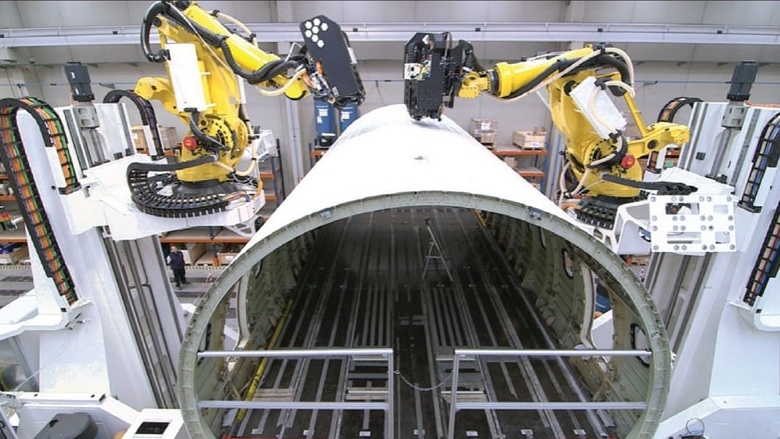

The increasingly sophisticated capabilities of robots will eventually eliminate some human tasks, but not all. In addition, 25% of retailers have reported they will distribute robots to free up workers from repetitive tasks.
Some robot companies often integrate various sensors into a smart space, which allows the entire process to be completed in one place in much less time.
For more than two decades, Hanson Robotics has been creating the most human-like robots in the world.
Now, scientists from the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and Harvard University’s West Institute of Bioengineering have discovered a new form of biological reproduction and used their findings to create the first self-replicating living robot.
A group of scientists developed a cake-shaped robot that can jump several times per second, which is seven and a half centimeters larger than its height.
They can have their own customizable controls and their own processor architecture, including patented technology, robotic arms, and CNC computers. Robot workers can be divided into robotics and roboticists. Most roboticists (people who make robots) to use more precise definitions.
Telechir is a complex robot, remotely controlled by a human operator, used in a telepresence system.
Mechatronics can help engineers build high-tech products such as industrial robots. Mechatronics disciplines combine knowledge and skills in mechanical, electrical engineering, and computing to create high-tech products, such as industrial robots.
SuperDroid Robots offers tactical robots of various sizes and budgets.
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) automates repetitive tasks, so employees can focus on more important tasks. They can help people do whatever they need and complete complex tasks we never knew existed.
From the 2005 animated movie Robots. Following Bigwelds’ directions to “see the need, fill the need,” Rodney develops a small flying robot called Wonderbot to help his father, who works as a dishwasher in a restaurant. To help Herb repair the damage, Rodney decides to move to Robot City, hoping to introduce Wonderbot to Bigweld Industries. Upon arriving in Robot City, Rodney kicked out Bigweld Industries by current company boss Phineas T. Ratchet, who, in Bigwelds’ absence, stopped manufacturing parts and inventing in favor of costly “upgrades” so that “obsolete” robots could not or would not pay them.

They learned that the evil robot that took over the Bigwelds factory was planning to destroy all the old robots they couldn’t afford to upgrade, so it was almost the entire city. Rodney travels to the big city to meet Bigweld and become an inventor, but eventually meets a few robots that are nothing, including his best new friend Fender. The story tells the story of a robot named Rodney Copperbottom looking for his idol at his company in Robot City, only to discover that its new owner conspired to trick the old robot into buying expensive upgrades. The robot was also nominated for the Youth Choice Award and the Visual Effects Association Award.
Whose to say that Robots we imagine today cannot become our future. In many ways it already has.
Cited Sources
- https://www.ssla.co.uk/robot/
- https://www.britannica.com/technology/robot-technology
- https://science.howstuffworks.com/robot.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robots_(2005_film)
- https://www.npr.org/2021/12/01/1060027395/robots-xenobots-living-self-replicating-copy
- https://x.company/projects/everyday-robots/
- https://www.hansonrobotics.com/hanson-robots/
- https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/robot
- https://www.nytimes.com/2021/12/07/science/robots-pancake-jump.html
- https://wyss.harvard.edu/news/team-builds-first-living-robots-that-can-reproduce/
- https://www.superdroidrobots.com/
- https://builtin.com/robotics
- https://www.technologyreview.com/topic/artificial-intelligence/robots/
- https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0358082/
- https://www.motoman.com/en-us/products/robots/industrial

robolo
says:Evil robot is terrific!